TWO CRYSTAL
STRUCTURES OF D(GICGAGAGC) SUGGEST THAT POTASSIUM IONS MEDIATE TO
FORM DNA OCTAPLEX WITH I-MOTIF OF GUANINE QUARTET
Jiro Kondo,
Shun-ichi Umeda, Tomoko
Sunami and Akio Takénaka
Graduate School
of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Midori-ku, Yokohama
226-8501, Japan (jkondo@bio.titech.ac.jp)
DNA structures have been described in
duplex forms, the two strands being aligned in the anti-parallel fashion, in
general. As a special case, the
telomeric DNA is assumed to form quadruplex with G-quartet and intercalated
cytosine motifs (i-motif).
In DNA replications, triple helix formation is required. Functional DNA would have much more
complicated structures. In the
present study, the two forms of crystal structures of d(GICGAGAGC)
have been determined by X-ray analyses, to investigate the structural basis for
such specific functions.
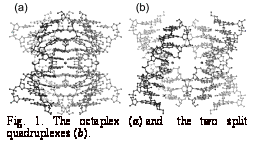
 The octamer of d(GICGA GAGC)
crystallizes in the two different forms with the space groups of I422 and I222,
depending on potassium-ion con-centration. In the I422 crystal, which is obtained at relatively low
potassium concentration, the octamers are assembled into an octaplex (Fig. 1a) that has
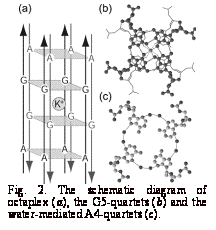
never been found as the nucleic acid structure. In the central part of this novel octaplex, the G5 residues
are associated around the crystallographic 4-fold axis to form the G-quartets
(Fig. 2b). A potassium
ion occupies the center of the octaplex for interactions with the eight O6
atoms of the G5 residues. The A4
residues also form water-mediated A-quartets (Fig. 2c) above and
below the two G5-quartets. Here it
is interesting to note that the octaplex is composed of the two quadruplexes,
each consisting of the four parallel strands with G-quartet. The two G-quartets are intercalated
into another with opposite strand polarity to form an I-motif of
G-quartets (Fig. 2a).
The octamer of d(GICGA GAGC)
crystallizes in the two different forms with the space groups of I422 and I222,
depending on potassium-ion con-centration. In the I422 crystal, which is obtained at relatively low
potassium concentration, the octamers are assembled into an octaplex (Fig. 1a) that has
never been found as the nucleic acid structure. In the central part of this novel octaplex, the G5 residues
are associated around the crystallographic 4-fold axis to form the G-quartets
(Fig. 2b). A potassium
ion occupies the center of the octaplex for interactions with the eight O6
atoms of the G5 residues. The A4
residues also form water-mediated A-quartets (Fig. 2c) above and
below the two G5-quartets. Here it
is interesting to note that the octaplex is composed of the two quadruplexes,
each consisting of the four parallel strands with G-quartet. The two G-quartets are intercalated
into another with opposite strand polarity to form an I-motif of
G-quartets (Fig. 2a).
In the I222 crystal, however, the
octaplex is split away into two quadruplexes with two potassium ions (Fig. 1b), each of
which contains two G-duets
bound to the respective potassium.
The two crystal forms suggest a dynamic transition from
quadruplex to octaplex in solution. In any forms, the two
adjacent anti-parallel strands form a zipper-like duplex
containing two contiguous G:C pairs and a sheared G:A pair at the both ends.