STUDIES OF
PROTEINS OF THE FOLATE BIOSYNTHESIS PATHWAY
Jacqueline F. Satchell, Brian J. Smith, Jonathan Baell, and Peter
M. Colman
The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute, Structural Biology Division. 1G
Royal Parade, Parkville, Victoria, 3050, Australia (satchell@wehi.edu.au).
Organisms parasitic upon humans, such as Plasmodium and Pneumocystis, are responsible for some of the world’s major health problems. These infections have commonly been treated with a class of compounds known as antifolates[1]. These inhibitors block the enzymes of the folate biosynthesis pathway causing decreased pyrimidine synthesis resulting in reduced DNA, serine and methionine formation, ultimately resulting in growth inhibition[2].
The
structures of several prokaryotic folate biosynthesis enzymes are available,
and allow for preliminary hypotheses to be drawn regarding likely inhibitors of this pathway. Docking
experiments have been conducted in order to determine whether DHP-analogues,
previously shown in E. coli
to be formed by the consensation of the substrate DHPP with sulfa drugs (shown
in figure 1), are capable of inhibiting this pathway. These compounds have been
chemically synthesised and have shown to have activity against dihydrofolate
reductase (DHFR) in yeast[3].
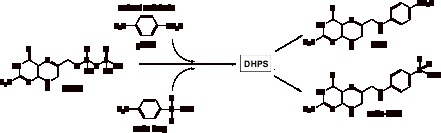
Figure 1 – Formation of DHP-analogues in vivo.
Pneumocystis carinii combines enzymes of this pathway in a more elaborate protein complex, the FAS protein, which incorporates hydroxymethyldihydropterin pyrophosphokinase (PPPK), dihydroneopterin aldolase (DHNA) and DHPS. Existing prokaryotic structures have also provided useful information with regards to the design of constructs for expression of this protein in insect cells. The structure of this protein will provide useful information from which drugs can be designed to target parasitic organisms.
References
1
Olliaro,P., Cattani, J. and Wirth, D. JAMA. 1996, 275, 230-234.
2 Volpe, F., Ballantine, S.P. and Delves, C.J. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 216, 449-458.
3 Patel O., Satchell J.F., Coloe P., Baell J. and Macreadie I. Microbial Drug Resistance. Accepted for publication in 2003.