SIMULATION OF
COMPTON DOUBLE SCATTERING
Yukinobu Kakutani, Akihisa Koizumi and
Nobuhiko Sakai
Graduate School and Faculty of Science, Himeji
Institute of Technology, Hyogo 678-1297, Japan
(yukinobu@sci.himeji-tech.ac.jp).
In 1987, a simulation of
magnetic Compton double scattering of circularly polarized photons by magnetic
electrons was reported by Sakai[1]. This simulation code was suitable for the
magnetic Compton scattering (MCS) experiments using gamma-ray sources, in which
no linear polarization of the incident gamma-rays presented.
We have made a new simulation
code including both linear and circular polarizations of incident photons,
which is suitable for the MCS experiments utilizing synchrotron radiation
x-rays.
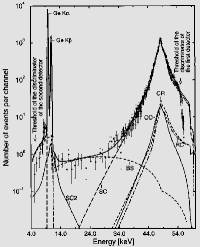
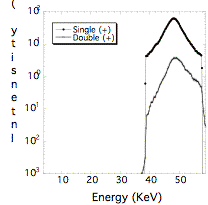
First, the validity of the
present simulation was confirmed by the reproducction of the experimental ratio
between Compton double scattering result on Ge measured by Pasic et al[2]. The agreement between the simulation and
experimental result is good, as shown in Fig. 1. Second, it was confirmed that
the intensity of Compton double scattering depends on polarization of incident
photons, material, incident energy and sample volume.
 Concerning
to the spin-dependent Compton double scattering, a result of simulation on Fe
(2 mm height, 10 mm wide and 10 mm thickness), showed that the influence of
magnetic Compton double scattering on 3d transition metal is negligible for
ordinary measurements.
Concerning
to the spin-dependent Compton double scattering, a result of simulation on Fe
(2 mm height, 10 mm wide and 10 mm thickness), showed that the influence of
magnetic Compton double scattering on 3d transition metal is negligible for
ordinary measurements.
(a)
(b)
Fig.1: Results of Compton double
scattering on Ge. (a) present simulation, a Lorenz type function is assumed to
simulate Compton broadening. (b) experiment by Pasic et al[2].
References
1
Sakai, N., (1987)
J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 56, 2477-2485.
2
Pasic, S and
Ilakovac, K., (1997) Phys. Rev. A 55, 4248-4252.